Stressful situations are an unavoidable part of modern life, yet the way we respond to them can dramatically influence our mental health, relationships, and overall well-being. Reducing Reactivity with Mindfulness is a practical approach that helps individuals pause, observe their internal experience, and choose responses more deliberately rather than reacting automatically. This article introduces the concept of reactivity, explains how mindfulness changes our relationship with stress, and offers insight into developing calmer, more thoughtful responses in everyday life.
Understanding Reactivity and the Stress Response
Reactivity refers to the automatic emotional and behavioral responses that occur when we perceive a threat, challenge, or discomfort. These reactions are rooted in the brain’s survival mechanisms. When stress arises, the nervous system activates a rapid response designed to protect us, often before conscious thought has time to intervene. While this response is useful in truly dangerous situations, it can be counterproductive in everyday interactions.
Common examples of reactivity include snapping in conversation, feeling overwhelmed by minor setbacks, or experiencing lingering emotional distress after stressful events. These reactions are often disproportionate to the situation and may lead to regret, strained relationships, or ongoing anxiety.
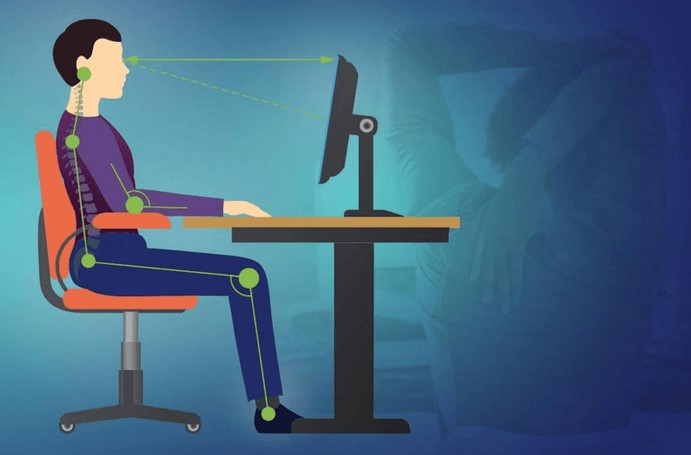
Stress-related reactivity is amplified by modern conditions such as constant digital stimulation, time pressure, and information overload. When the nervous system rarely has time to reset, the threshold for reactivity lowers. Small stressors accumulate, making emotional responses more intense and frequent.
Mindfulness offers a way to interrupt this cycle. Rather than suppressing emotions or forcing calm, mindfulness encourages awareness of internal experiences as they arise. This awareness creates a critical pause between stimulus and response, allowing for choice rather than compulsion.
How Mindfulness Changes the Stress Experience
Mindfulness is the practice of paying attention to present-moment experience with openness and without judgment. When applied to stress, it shifts how individuals relate to thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations. Instead of being swept away by reactions, mindfulness allows them to be observed.
From a neurological perspective, mindfulness strengthens areas of the brain involved in emotional regulation and self-awareness. Regular practice reduces overactivation of the brain’s threat centers while enhancing the ability to assess situations more calmly. This does not eliminate stress but changes how it is processed.
Mindfulness also increases sensitivity to early stress signals. Many reactive behaviors occur because individuals notice stress only after it has escalated. By tuning into subtle cues—such as muscle tension, shallow breathing, or racing thoughts—mindfulness allows for earlier intervention. Addressing stress at this stage requires less effort and reduces emotional intensity.
Importantly, mindfulness fosters acceptance rather than resistance. Stress often intensifies when individuals fight against their emotional responses. Acknowledging stress with curiosity rather than judgment can reduce its grip. This acceptance does not mean approval of difficult circumstances, but recognition of reality as it is in the moment.
Practical Mindfulness Skills for Everyday Stress
Mindfulness does not require withdrawing from daily responsibilities. Instead, it can be integrated into ordinary moments, making it especially useful for managing real-life stressors.
One foundational skill is mindful breathing. By gently focusing attention on the breath, individuals create a physical anchor that stabilizes attention. Slow, intentional breathing signals safety to the nervous system, helping reduce physiological arousal. This practice can be used discreetly during conversations, meetings, or transitions.
Another key skill is emotional labeling. Silently naming emotions such as frustration, anxiety, or disappointment helps create distance from them. Research shows that this simple act can reduce emotional intensity by engaging cognitive processing. Rather than being consumed by emotion, individuals become observers of their experience.
Body awareness is equally valuable. Stress often manifests physically before it becomes mentally overwhelming. Noticing posture, muscle tension, or jaw clenching can prompt gentle adjustments that release built-up stress. This awareness reinforces the connection between mind and body.
Finally, mindful questioning supports thoughtful responses. Asking simple internal questions like “What is actually happening right now?” or “What response aligns with my values?” shifts focus from impulse to intention. These questions create space for wiser action, even under pressure.
Applying Mindfulness to Build Long-Term Resilience
Reducing reactivity is not about achieving constant calm. It is about increasing flexibility in how one responds to stress over time. Mindfulness strengthens this flexibility by promoting self-awareness, emotional tolerance, and intentional action.
As mindfulness becomes habitual, individuals often notice improved relationships. Pausing before responding allows for clearer communication and greater empathy. Misunderstandings are less likely to escalate, and conflicts can be approached with greater composure.
Mindfulness also supports mental health by reducing chronic stress patterns. When reactions are less intense and shorter in duration, the nervous system spends more time in a regulated state. This balance supports better sleep, concentration, and emotional stability.
Crucially, progress in mindfulness is gradual. Reactivity will still occur, especially during high-stress periods. The goal is not perfection but awareness. Each moment of noticing reactivity without judgment is itself a step toward greater calm and clarity.
Stress may be inevitable, but automatic reactivity does not have to be. By cultivating awareness, mindfulness provides the tools needed to pause, observe, and choose responses more wisely. Reducing Reactivity with Mindfulness supports emotional regulation, clearer thinking, and healthier relationships by transforming how stress is experienced rather than trying to eliminate it. With consistent practice, mindfulness becomes a steady resource for responding to life’s challenges with greater calm, intention, and resilience.




 In today’s healthcare landscape, the focus is gradually shifting from reactive treatment to proactive prevention. Preventive care incentives are playing a crucial role in encouraging individuals to take charge of their health before problems arise. Prevention, rather than waiting for symptoms to show up or illness to develop, has proven to be an effective strategy in reducing the burden of chronic diseases, minimizing healthcare costs, and improving overall quality of life. This shift toward preventive care is not only beneficial for individuals but also for healthcare systems at large, which can reduce their overall expenditure by focusing on prevention rather than expensive treatments for preventable conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of preventive care, the incentives available for individuals, and how embracing a preventive approach to health can help you live a longer, healthier life.
In today’s healthcare landscape, the focus is gradually shifting from reactive treatment to proactive prevention. Preventive care incentives are playing a crucial role in encouraging individuals to take charge of their health before problems arise. Prevention, rather than waiting for symptoms to show up or illness to develop, has proven to be an effective strategy in reducing the burden of chronic diseases, minimizing healthcare costs, and improving overall quality of life. This shift toward preventive care is not only beneficial for individuals but also for healthcare systems at large, which can reduce their overall expenditure by focusing on prevention rather than expensive treatments for preventable conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of preventive care, the incentives available for individuals, and how embracing a preventive approach to health can help you live a longer, healthier life.